Not all window attachment products and product categories are the same, and the way they convey their energy saving message and data shouldn’t be either. Through the AERC Certification Program there are a number of factors and metrics that go into the rating and certification of each product. U-Factor and the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) are important metrics for interior shade products for cellular, slate, and pleated. Meanwhile, Visual Transmittance is a key factor for exterior shade products like roller shutter, fixed solar screens, and roller shades. However, all AERC certified products take their main product rating from the “Cool Climate” rating and the “Warm Climate” rating. There’s a lot to compare, but we broke it down for you below and have explained what these metrics and numbers mean, and how they can assist with your window attachment product purchase decision.
What do Warm Climate Ratings and Cool Climate Ratings Mean?
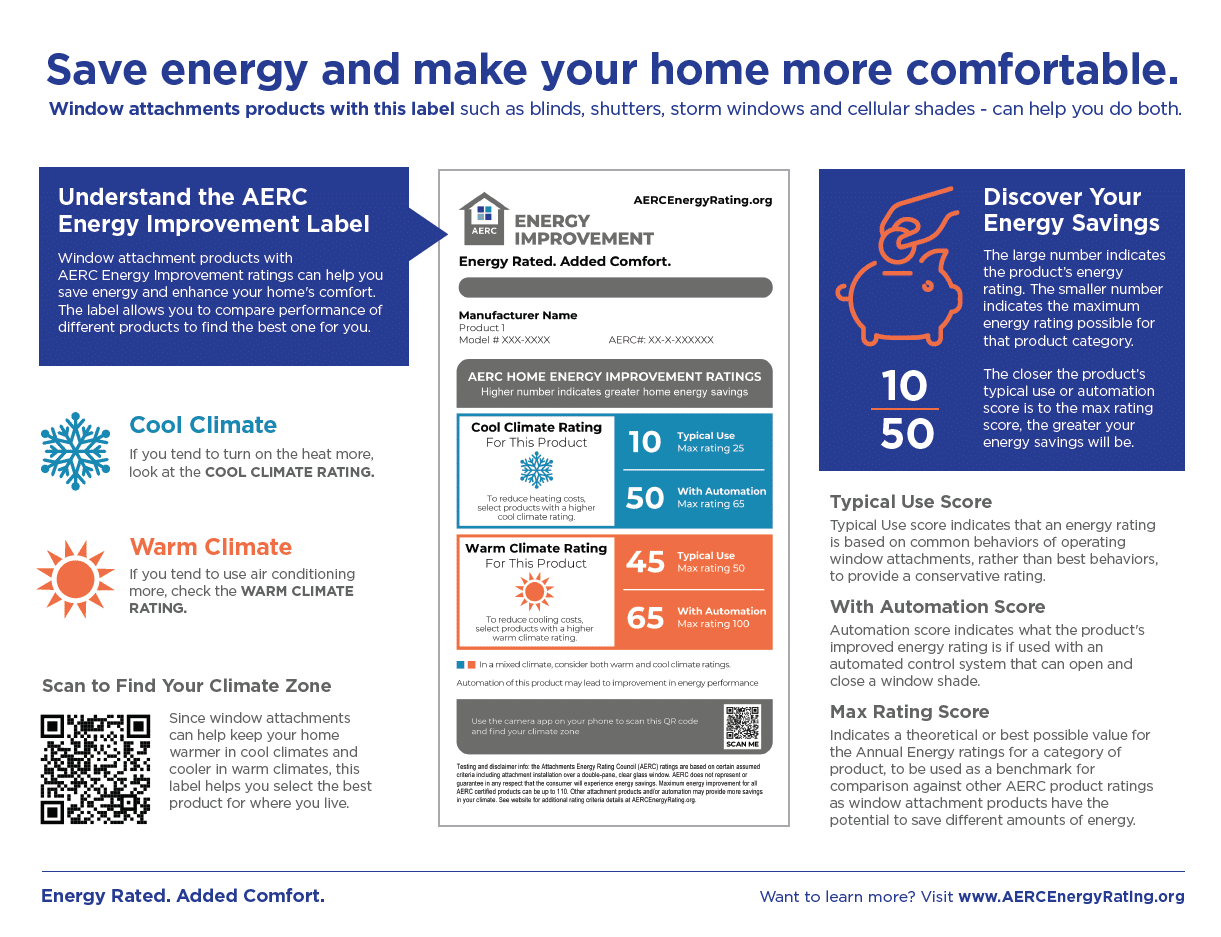
Any product with a Cool Climate or Warm Climate rating above zero (0.00) can save you energy compared to not using a window attachment at all.
The “Cool Climate” rating indicates your potential energy savings when using that particular window attachment when it’s cooler outside, and you may be required to turn up the heat. Higher energy improvement rating numbers, and those that are closer to the maximum (max) for that product category, are rated to provide greater energy savings.
The “Warm Climate” rating indicates your potential energy savings when using that particular product when it’s warmer outside, and your home may use more air conditioning. Higher energy improvement rating numbers, and those that are closer to the maximum (max) for that product category, will provide greater energy savings.
For window attachments that are automated, the label will indicate the improved energy rating with automation to the right of the energy rating number. This shows what the product’s energy rating is if used with automation.
Reaching the “Max”
Different window attachment products have the potential to save different amounts of energy. Therefore, every product category has a different “Max Improvement” number, or maximum possible energy rating. For example, if you live in a cool climate and are buying a storm window, the Max Improvement number you can expect for that product category is 110; if you are shopping for new blinds, on the other hand, the Max Improvement number you can expect is 15. The closer the product’s energy rating is to the Max Improvement number for its product category, the better that product is in terms of energy savings relative to others within its category.
Looking to compare energy improvement across different product categories (i.e. storm windows vs. blinds)? Simply compare the Cool Climate or Warm Climate ratings on each product label, depending on the climate in which you live.
Not Applicable?
If the words “Not Applicable” appear on the label, this indicates the product is not recommended for energy improvement in that particular climate. When a window attachment product is “Not Applicable for Energy Improvement,” this may mean that product was designed for use in a particular climate or designed to address specific conditions.
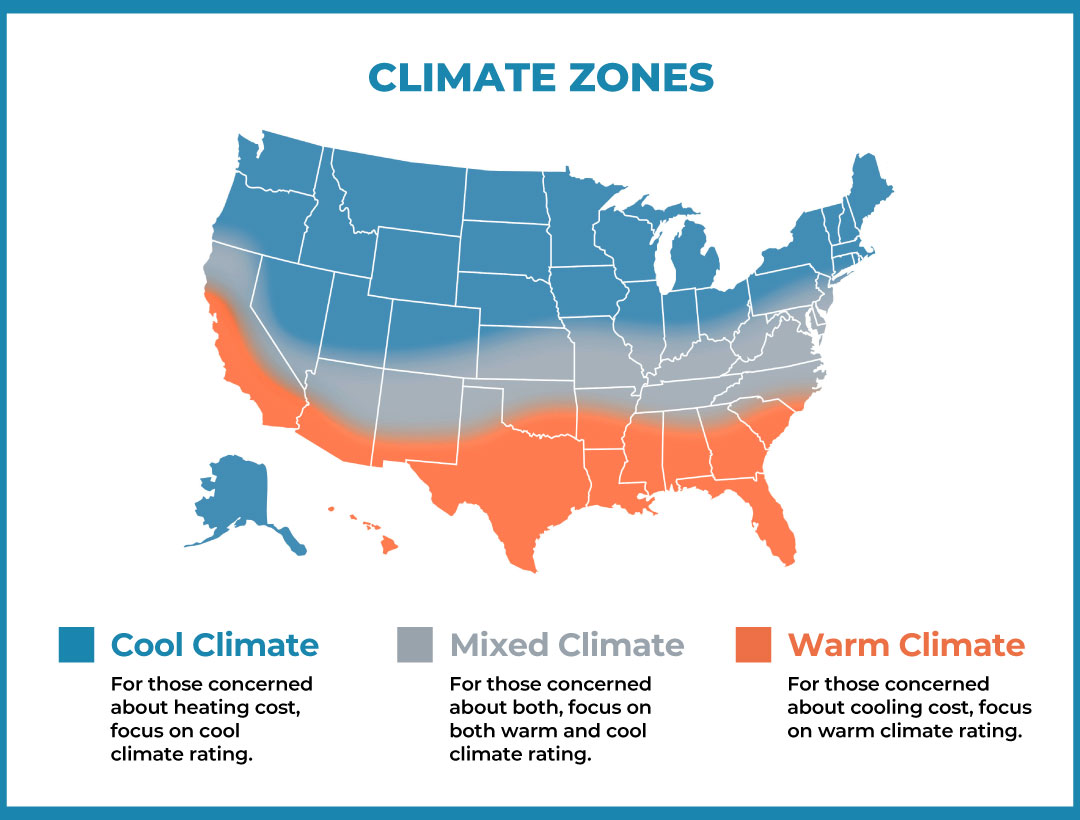
Use the camera app on your phone to scan this QR code to find your climate zone to determine the AERC Rating that works best for your needs.
U-Factor
Measures how well a product can retain heat and keep it from escaping from inside a room. Products with lower U-Factors block heat loss and should be considered when cool climate heating costs are a concern.
Range: 0.20-1.20
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
Measures how well products resist unwanted heat gain. Products with lower SHGC may reduce cooling costs. Products with higher SHGC, by contrast, may reduce heating costs due to passive solar heating.
Range: 0.00-1.00
Visual Transmittance:
Measures how well a product is designed to light your home with daylight. Products with higher VT allow more daylight to enter and may reduce the need for artificial lighting, another important factor in reducing utility costs.
Range: 0.00-1.00
Air Leakage:
Measures how much air will pass through a product. Products with lower air leakage may result in fewer drafts and help reduce heating costs.